The eukaryotic cell cycle and cancer overview answer key – Delving into the intricacies of the eukaryotic cell cycle and its profound implications in cancer development, this comprehensive overview unveils the intricate dance of cellular life and the devastating consequences of its disruption.
The eukaryotic cell cycle, a meticulously orchestrated sequence of events, ensures the orderly growth, division, and death of cells. However, when this delicate balance is disrupted, the uncontrolled proliferation of cells can lead to the insidious disease known as cancer.
1. Introduction

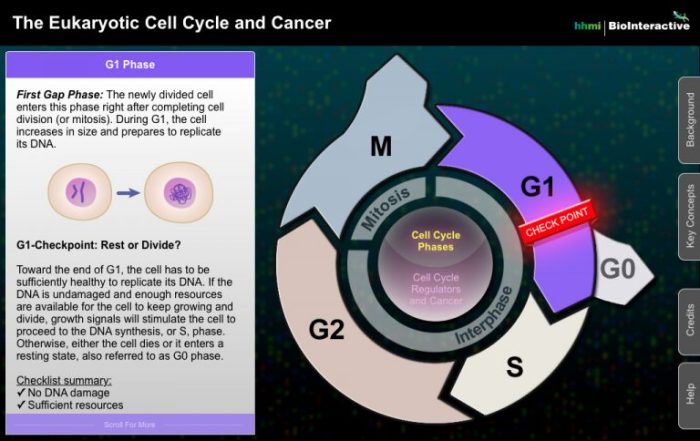
The eukaryotic cell cycle is a fundamental process that governs the growth, development, and reproduction of all eukaryotic organisms. It is a precisely orchestrated series of events that ensures the faithful duplication and distribution of genetic material to daughter cells.
The cell cycle is divided into distinct stages: the interphase, which includes the G1, S, and G2 phases, and the mitotic phase, which includes prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During interphase, the cell grows and prepares for division, while during the mitotic phase, the cell divides into two daughter cells.
2. Cell Cycle and Cancer
The cell cycle is tightly regulated by a complex network of checkpoints and signaling pathways. Disruptions in these regulatory mechanisms can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and division, which is a hallmark of cancer.
Mutations in genes that encode cell cycle regulators can lead to the development of cancer. For example, mutations in the tumor protein p53, a key regulator of the G1/S checkpoint, can lead to the development of a variety of cancers.
3. Cancer Overview, The eukaryotic cell cycle and cancer overview answer key
Cancer is a disease characterized by the uncontrolled growth and division of cells. It can arise in any organ or tissue of the body and can manifest in a variety of forms, including solid tumors, leukemias, and lymphomas.
Some common types of cancer include breast cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer, colon cancer, and leukemia.
4. Cell Cycle Regulation and Cancer Treatment
Understanding the cell cycle has provided important insights into the development of cancer treatments. By targeting specific cell cycle regulators, it is possible to inhibit the growth and division of cancer cells.
Some examples of cancer treatments that target the cell cycle include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy. Chemotherapy drugs can damage DNA, which can lead to cell death. Radiation therapy can also damage DNA and can be used to kill cancer cells.
Targeted therapy drugs are designed to inhibit specific cell cycle regulators, such as the cyclin-dependent kinases.
FAQ Insights: The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle And Cancer Overview Answer Key
What is the significance of the eukaryotic cell cycle?
The eukaryotic cell cycle is essential for maintaining tissue homeostasis, ensuring proper growth and development, and facilitating the repair of damaged cells.
How does cell cycle dysregulation contribute to cancer?
Mutations in genes encoding cell cycle regulatory proteins can lead to uncontrolled cell proliferation, a hallmark characteristic of cancer.
What are the key characteristics of cancer?
Cancer is characterized by uncontrolled cell growth, invasion of surrounding tissues, and the ability to metastasize to distant sites.